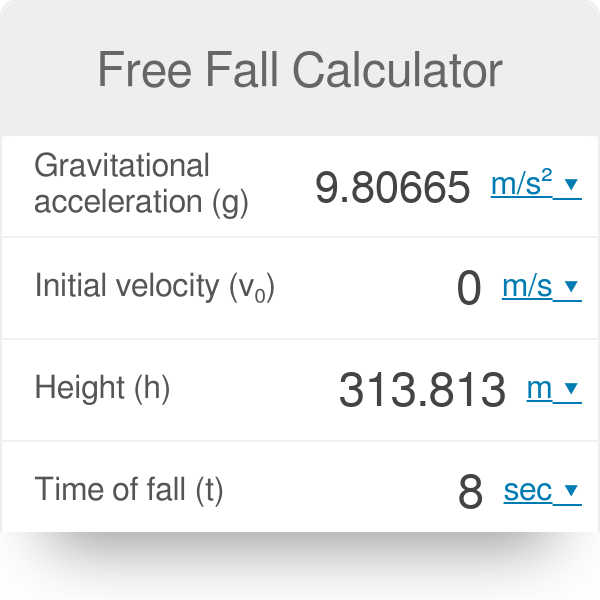
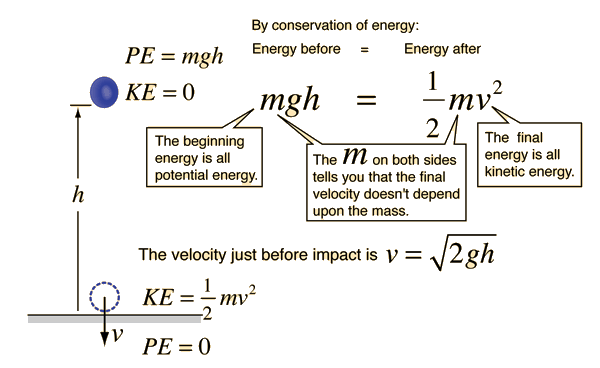Find the free fall distance using the equation s 05 g t² 05 980665 8² 3138 m. By ron kurtus revised 31 march 2017 when you drop an object from some height above the ground it has an initial velocity of zero.

Energy Forces And Vectors
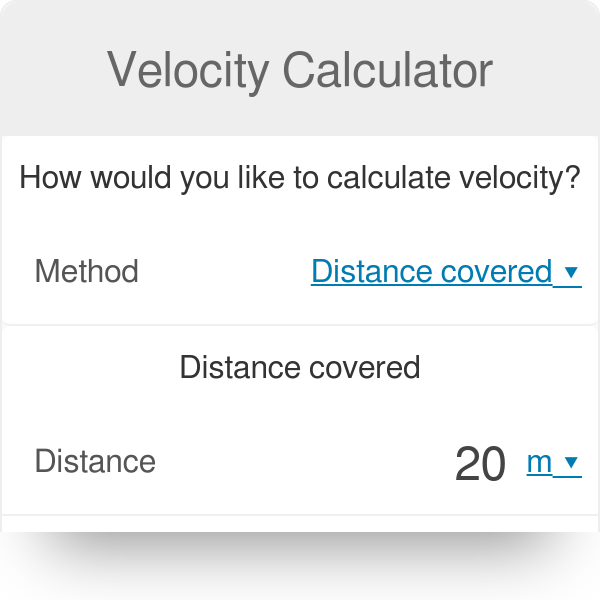
Velocity weight height equation. Velocity is the rate by which the displacement of the object changes. 1 20200614 1147 female 20 years old level an office worker a public employee useful. This equation tells us how the batted ball velocity v 1adepends on the mass of the ball m 1 and bat m 2 the elasticity of the ball e the pitched ball speed v 1b and the bat swing speed v 2b. If you know the height from which the object is falling but dont know the time of fall you can use this calculator to find it too. Since a 32 feet per second squared the equation becomes t 1032. The value of t is 031.
Subtract your result from the objects initial upward velocity. 50 98 48 meters per second. For example if the initial upward velocity is 50 meters per second it would be. The positive direction is upwards so the weight is preceded by a negative sign. A negative velocity means it is moving downward falling which is exactly what we would expect. Where w is the weight m is the mass v is the vertical velocity t is the time a is the acceleration and f is the net external force.
The velocity of the object at rest is zero. In this example you discover that it takes 031 seconds for a projectile to reach its maximum height when its initial velocity is 10 feet per second. The height velocity formula for generating these curves is hv text percentile m 1 lsz 1l h v percentile m 1ls z1l where hv is height velocity m is the median average l is a quality called skewness s is variability and z is the chosen standard deviation from the mean. The equations assume. Simple equations allow you to calculate the velocity a falling object reaches after a given period of time and its velocity at a given displacement. The properties of the ball may be treated as constants since they dont change during a turn at bat.
The velocity is zero if the initial and final position of the object is same. The equation for orbital velocity is v square root gm r where v is the linear velocity g is the gravitational constant m is the mass of the earth and r is the distance from the earth to the satellite the moon in this case 382 x 106 metres so look up values for g m plug them into the equation youll get an answer. T 10 a. This answer is the objects velocity. Velocity equations for falling objects.