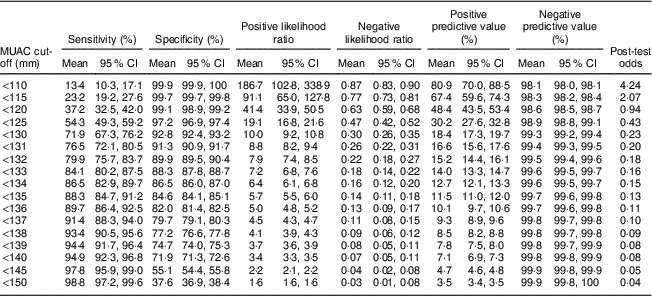
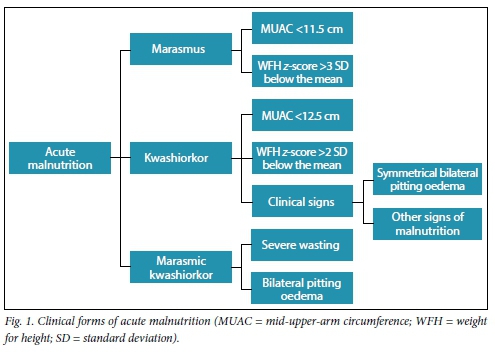
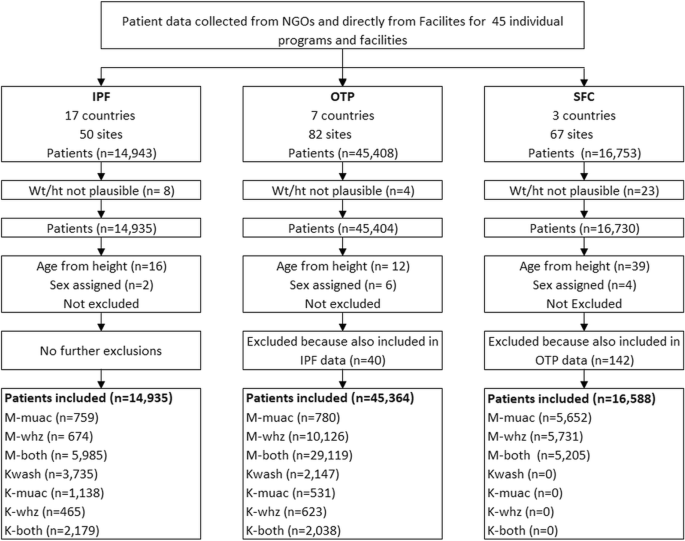
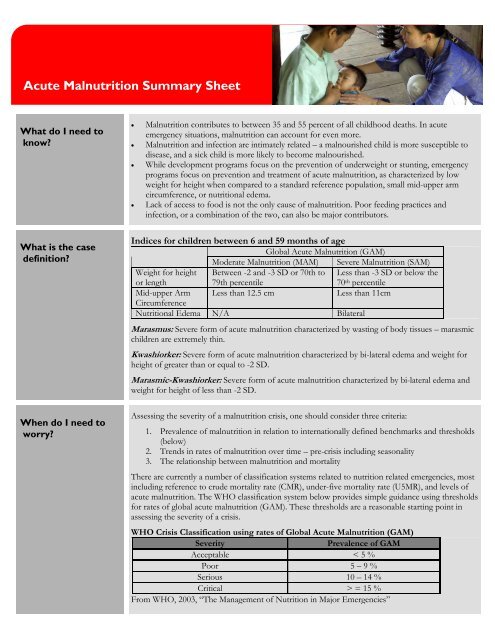
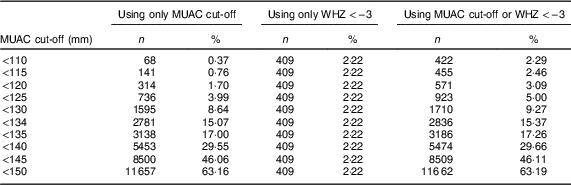
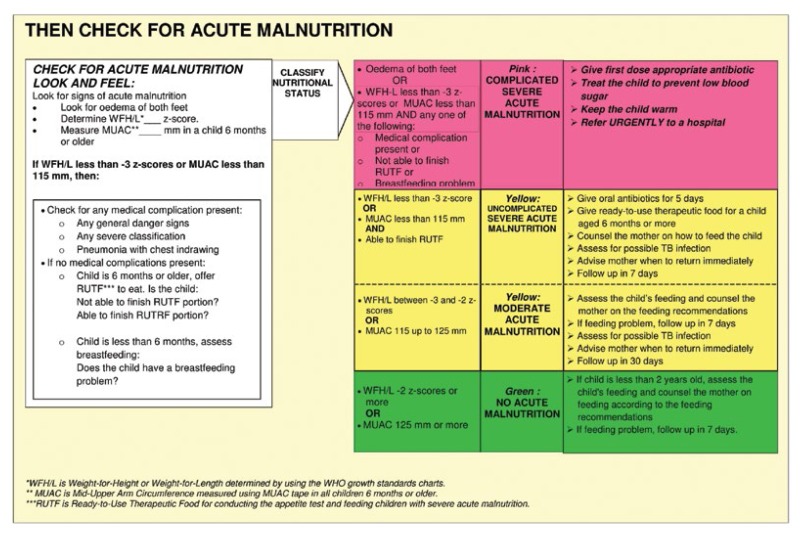
Wasting or thinness indicates in most cases a recent and severe process of weight loss which is often associated with acute starvation andor severe disease. A mid upper arm circumference 125 mm muac 125 or a weight for height z score2 whz 2 correlate poorly.

Guidance Note On The Temporary Dual Use Of Rutf For The
Weight for height acute malnutrition. However wasting may also be the result of a chronic unfavourable condition. 11 this value is compared to reference values that can gauge whether a person is healthy or malnourished. We aimed at assessing the contribution of age sex stunting height for age haz2 and low sitting standing height ratio z score ssrz in the 1st tertile of the study population called hereafter longer legs to this diagnosis discrepancy. The world health organisation who recommends weight for lengthheight wflh represented as a z score for diagnosing acute malnutrition among children aged 0 to 60 months. A person is deemed undernourished if they have a bmi under 185 and is severely undernourished with a bmi under 16. The current definitions of acute malnutrition are based either upon a weight for height z score whz below 2 standard deviations of the international reference population world health organization 2006 growth standards or a mid upper arm circumference muac lower than 125 mm.
Under controlled conditions weight height and length measurements have high degree of reliability. The two anthropometric indicators of acute malnutrition in children under 5 years ie. These indicators are used independently to define the sum of. Bmi is calculated by dividing a persons weight in kilograms by their height in meters squared. Weight for height below 3 sd is a highly specific criterion to identify severely acutely malnourished infants and children.